Live Unicode checker
Stay safe with Xanthos
Accepted characters
These are characters you do expect to see in links
Additional charaters
These are characters you may expect to see in some languages
Warning characters
These are characters you do not expect to see
Good news
No non-Unicode characters have been identified
Warning
Non-Unicode characters have been identified. We recommend you do not follow this link unless you know it is safe.
Caution
Non-unicode characters have been identified, but these can be used in languages such as German and Swedish, so may be ok.
Please note that this resource is provided for guidance only. We do not check whether the website is safe for you to visit, it’s only checking the characters in the text you provide. Therefore any website you do, or do not, choose to visit after using this resource you do so with this understanding.
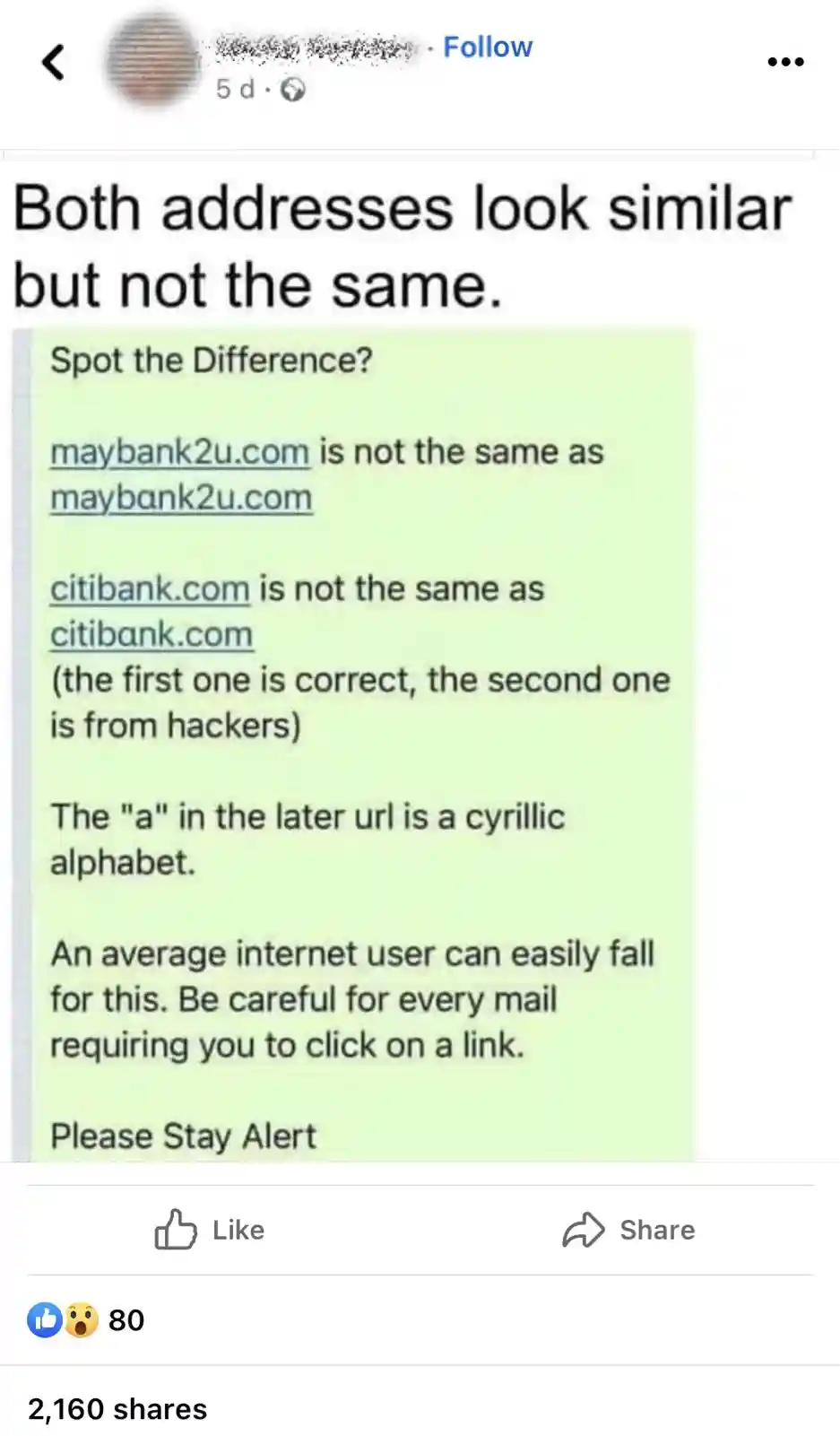
A sensible social media warning
The introduction of internationalised domain names was intended to make the internet more accessible to users around the world, allowing them to register domain names in their native scripts. While this inclusion can enhance inclusivity, it also raises concerns about potential misuse, particularly in the context of phishing and hacking.
One of the primary security concerns with allowing certain characters, such as Cyrillic, in URLs is the potential for homograph attacks. Homograph attacks involve the use of characters from different scripts that visually resemble each other, making it challenging for users to distinguish between them.
With simple changing of fonts a normal “a” and a Cyrillic “а” will look identical to the naked eye, but they represent different characters.
Look at the following links. Whilst they appear identical they are very different:
https://www.xanthosdigital.com/live-unicode-checker
https://www.xanthosdigital.com/livе-uniсоdе-chеckеr
https://www.xanthosdigital.com/live-unicöde-checker
https://www.xanthosdigital.com/livе-uniсödе-сhесkеr
Click on each link to see how they appear in the checker above (don’t worry, they’re not actual links) and reveal the safe one.
The social media warning says “An average internet user can easily fall for this”, but even highly experienced internet users would struggle to tell the difference.
Hackers and phishing attackers could exploit this visual similarity to create malicious URLs that mimic legitimate websites, tricking users into divulging sensitive information such as login credentials. This technique, known as IDN homograph attack, has been a concern since the inception of internationalised domain names.
It’s essential for users to stay vigilant and verify the legitimacy of websites, especially when clicking on links or entering sensitive information online.

